Chrome插件开发中的消息传递
最近在学习chrome插件的开发,学习到消息传递部分的时候颇费了一番功夫,试验了很多次,摸索了无数回。现把自己对消息传递机制的研究总结于此,希望对同样学习chrome插件开发的同学有所帮助。
学习新知识是一个既刺激又痛苦的过程,尤其是编程这一行。网上的教程,言论颇多,不乏经典,但也有很多错误之处,一句话就是鱼龙混杂。这样就给初学者的学习带来极大的额外学习成本。然而,当我们经过自己的努力,理解了或者解决了一个问题后,那种快感,也是只有程序员的你才能体会。
这篇文章是在自己动手实践的基础上完成的,结合源码和截图,可能大家更加容易理解些。当然,如果有错误之处,也请批评指正。
几个最基本的文件
在这里,先假设大家对chrome插件开发的最基本知识已有所掌握。例如什么是manifest.json,什么是background.html等。
manifest.json
{
"name": "A browser action with a popup that changes the page color.",
"version": "1.0",
"permissions":["tabs","<all_urls>"],
"browser_action": {
"default_icon": "icon.png"
},
"background": {
"page": "background.html"
},
"content_scripts": [
{
"matches": ["<all_urls>"],
"js" : ["jquery-1.7.1.js","injectscript.js"]
}
],
"manifest_version": 2
}
background.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>bg</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="bg.js"><script>
</head>
<body>
hello
<body>
</html>
这里引用了一个后台处理程序,bg.js,后面会讲到。
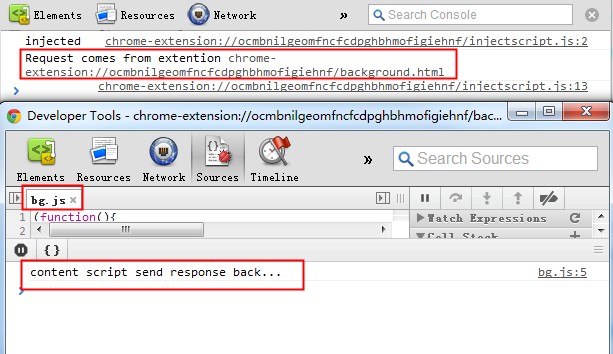
扩展程序发送请求数据到内容脚本,内容脚本给出回应
扩展程序后台脚本bg.js
(function(){
chrome.browserAction.onClicked.addListener(function(tab) {
// 扩展向内容脚本发送消息
chrome.tabs.sendMessage(tab.id,{
greeting: "hello to content script!"
}, function(response) {
console.log(response.farewell);
});
});
})();
内容脚本injectscript.js
(function(){
console.log("injected");
var resOK = {
farewell: "content script send response back..."
};
var resError = {
farewell: "content script hasError!"
};
chrome.extension.onMessage.addListener(function(request, sender, sendResponse) {
console.log("Request comes from extention " + sender.tab.url);
if (request.greeting === "hello to content script!"){
sendResponse(resOK);
}else{
sendResponse(resError);
}
});
})();
扩展程序向内容脚本发送一条消息hello to content script!,内容脚本接收到这条消息后去判断是不是那句话,如果是,就返回resOK对象,如果不是,就返回resError对象。
这时,扩展程序收到内容脚本的一条回应,至此,此番通话就结束了。
看一下结果截图
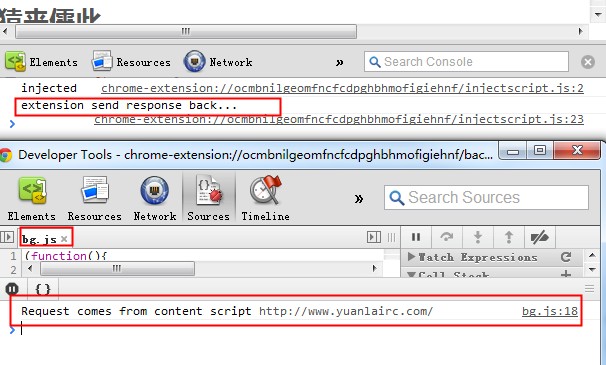
内容脚本发送请求数据到扩展程序,扩展程序给出回应
扩展程序后台脚本bg.js
(function(){
var resOK = {
farewell: "extension send response back..."
};
var resError = {
farewell: "extension hasError!"
};
chrome.extension.onMessage.addListener(function(request, sender, sendResponse) {
console.log("Request comes from content script " + sender.tab.url);
if (request.greeting === "hello to extention!"){
sendResponse(resOK);
}else{
sendResponse(resError);
}
});
})();
内容脚本injectscript.js
(function(){
console.log("injected");
chrome.extension.sendMessage({greeting: "hello to extention!"}, function(response) {
console.log(response.farewell);
});
})();
内容脚本向扩展程序发送一条消息hello to extention!,扩展程序接收到这条消息后去判断是不是那句话,如果是,就返回resOK对象,如果不是,就返回resError对象。
这时,内容脚本收到扩展程序的一条回应,至此,此番通话就结束了。
特别应该注意的是:扩展程序向内容脚本发送请求数据时用的是chrome.tabs.sendMessage,反过来,用的是chrome.extension.sendMessage。
看一下结果截图
如果以后还有一些chrome插件的学习总结,还会写在这里。